|
How Slow Cooking Works |
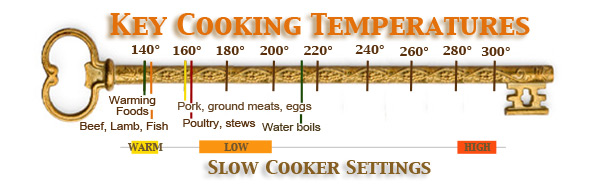
 Low Temperature Cooking Low Temperature Cooking - Slow cooking methods may well be called "Low Temperature" cooking. A slow cooker provides a stable environment where food is gradually brought to a temperature of 170-200°F on a low setting, or to 280-300°F on a high setting. By exposing food to only low temperatures for 7-10 hours, the food gradually reaches the temperature of its surroundings, cooking in the process. The result is perfectly cooked food.
Key Temperatures - Cooking is practical science in action. Key temperatures while cooking accomplish the necessary cooking tasks of tenderizing, killing bacteria, and releasing flavors. Below these temperatures, harmful bacteria may not be killed, and may even proliferate. Most stove cooking utilizes hot temperatures and seeks a suitable internal temperature quickly. Slow cooking begins with the end in mind and seeks an equilibrium between the cooking environment and the food.
Time vs. Temperature - In exchange for fast-cooking high temperatures, more time is required for the food to reach a safe cooking temperature and become tender. That's where the advantage of slow cooking becomes apparent. With low heat, food is started far ahead of eating time, and is able to be left unattended - a multi-tasker's dream.
|

|
Slow cooking excels in several ways:
(1) Tough to Tender Meats -- Tough, inexpensive meats become tender with slow cooking. Slow cooking softens the connective tissues gradually while preserving the tenderness of the muscle protein.
(2) Unattended Cooking - Assemble the ingredients, turn it on, and walk away! This feature is perhaps one of the biggest benefits of slow cooking. No stirring is required; there's little chance of burning at these low temperatures.
(3) One-pot Convenience - A one-pot meal is convenient to make and serve. It is energy efficient by nature and clean up is easy.
(4) Dried to Tender Beans - Beans provide great nutrition. Cook dried beans in a slow cooker to save money, to eliminate the soaking step, and to make beans more easily included in your diet. Canned beans are about four times as expensive as dried beans.
(5) Economical - Slow cookers utilize less expensive cuts of meat, access cheap bean nutrition, all while using a minimal amount of energy. The real economy comes at the end of the day knowing that supper is waiting at home and expensive eating out or carryout is an unneeded option. |
As great as slow cooking is, it is not appropriate or useful all of the time.
(1) Expensive Meat Cuts - Tender cuts of meat will not fare well in a slow cooker; use tough, inexpensive cuts for best results.
(2) Seafood Cooks Too Quickly - Seafood cooks quickly at low temperatures; the elongated heat of a slow cooker serves no purpose and can toughen the seafood. Add seafood at the end of slow cooking.
(3) Dairy Not Heat Tolerant - Milk and cheese may separate during long cooking. Add dairy ingredients at the end of cooking.
(4) Some Baking, Yes, Other Baking, No - Slow cookers can "bake" cakes and breads, but cannot turn out cookies, pies, and other pastries where higher temperatures are required.
(5) Browning Meats - Many meat dishes benefit from a browning step that sears the surface and produces flavorful caramelization. Slow cooking does not produce any tasty brown bits; some recipes call for a separate browning step prior to adding to the pot.
(6) Color Appeal - Slow-cooked foods often lose their color. Compensate with some vibrant garnishes.
|
 |
Overcooking - While it is nearly impossible to burn food while slow cooking, it is possible to overcook the food and have it become undesirable. Follow reliable recipes and suggested times. Slow-cooked dishes that are more forgiving and can patiently wait for you include soups, stews, beans, and larger cuts of meat. Grains, many vegetables, and desserts require timing that is more precise.
Storing Slow-Cooked Dishes - Once served, transfer any leftovers to a storage container, allow to cool, then refrigerate - all within 2 hours of completed cooking. (The heat-retaining properties of the crock make it unsuitable for cooling foods quickly enough). Slow cookers work too slowly to be useful in reheating foods. However, warmed foods can be kept warm in a pre-heated slow cooker. Pay attention to safe food practices regarding timing and temperatures. |
|
|

 Low Temperature Cooking - Slow cooking methods may well be called "Low Temperature" cooking. A slow cooker provides a stable environment where food is gradually brought to a temperature of 170-200°F on a low setting, or to 280-300°F on a high setting. By exposing food to only low temperatures for 7-10 hours, the food gradually reaches the temperature of its surroundings, cooking in the process. The result is perfectly cooked food.
Low Temperature Cooking - Slow cooking methods may well be called "Low Temperature" cooking. A slow cooker provides a stable environment where food is gradually brought to a temperature of 170-200°F on a low setting, or to 280-300°F on a high setting. By exposing food to only low temperatures for 7-10 hours, the food gradually reaches the temperature of its surroundings, cooking in the process. The result is perfectly cooked food.